Friso® Gold Comfort Next
Toddler


Young Adventurer
Friso® Gold Comfort Next
Toddler
-
Beta-PalmitinHelps with softer stool formation for more comfortable and regular movement1.
-
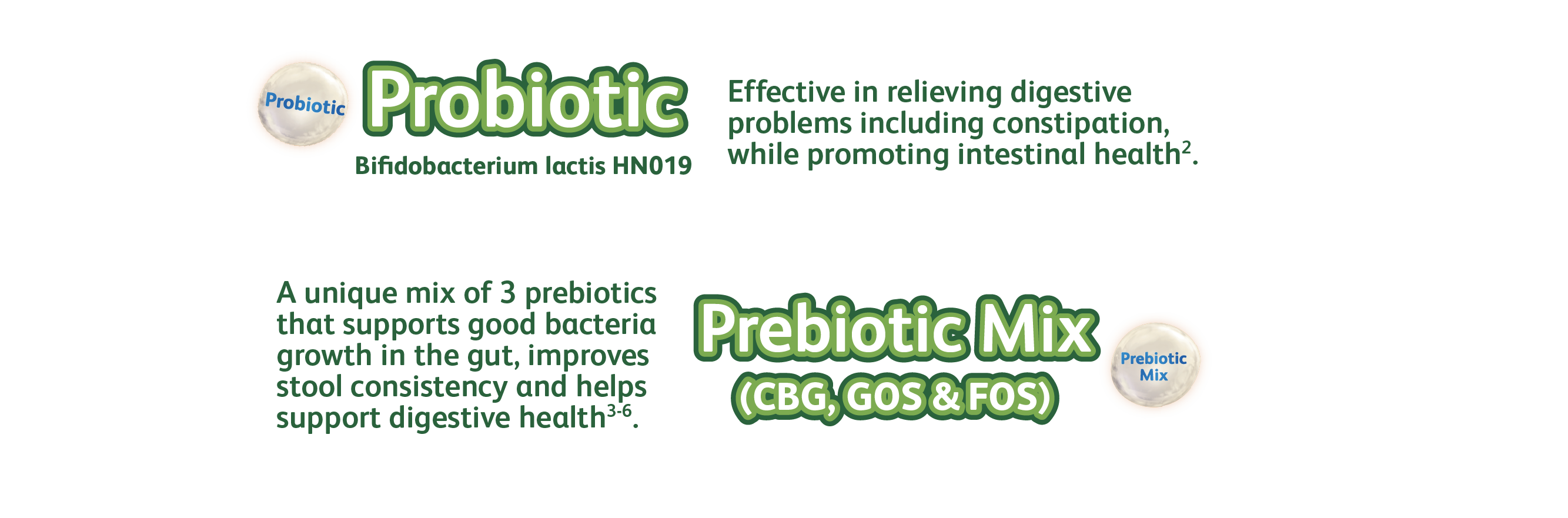
Probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis HN019Effective in relieving digestive problems including constipation, while promoting intestinal health2.
-
Prebiotic Mix (CBG, GOS & FOS)Supports good bacteria growth in the gut and improves stool consistency3-6.
-
Nucleotides, DHA, Vitamin D & IronSupports natural body defence, growth and development7.
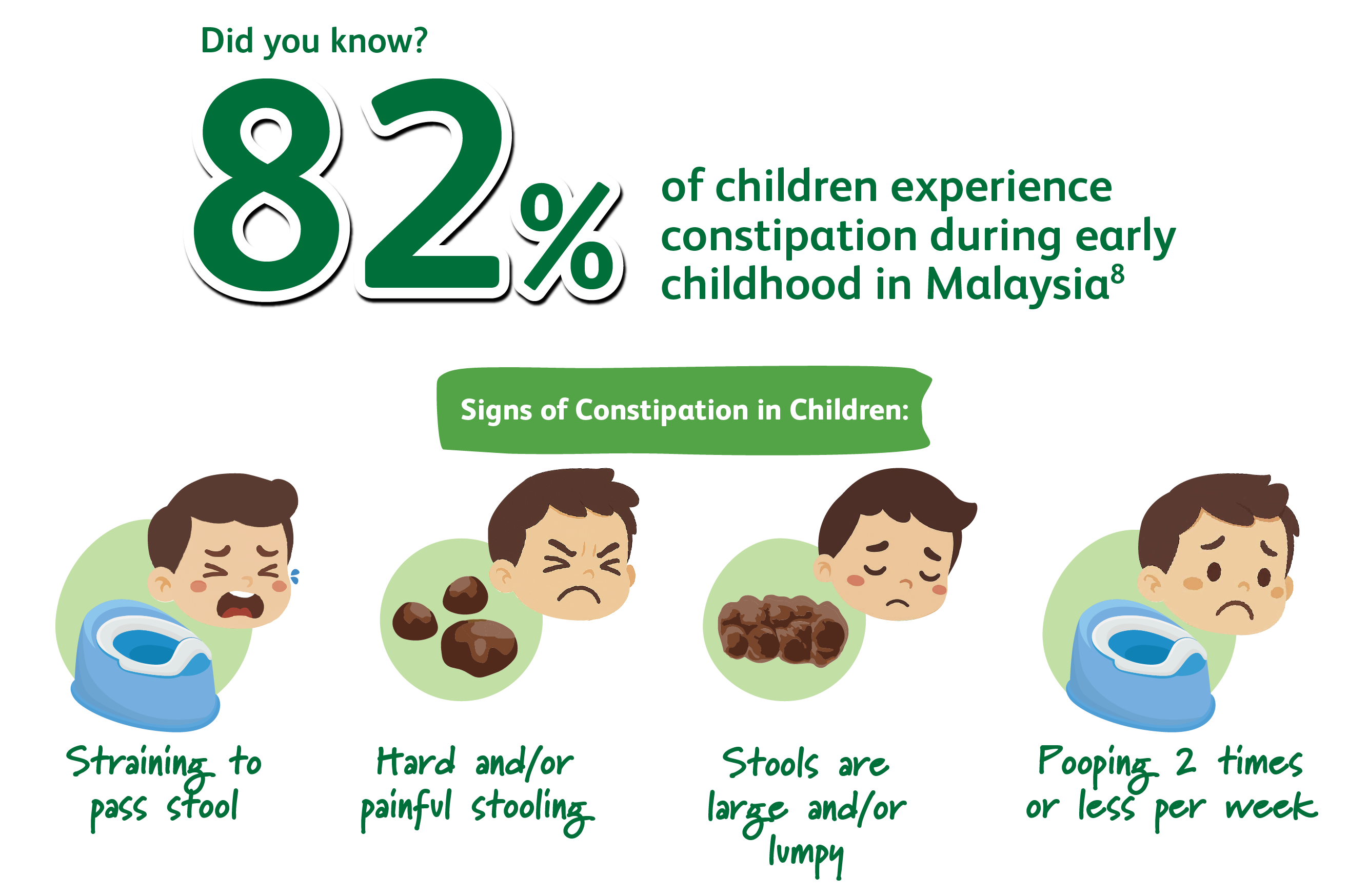

New Friso® Gold Comfort Next with Beta-Palmitin can help.
Beta-Palmitin, Pre and Probiotic mix help with softer stool formation,
improve stool consistency and have been proven effective in relieving constipation1-6.


Stools move easily without pain or difficulty.

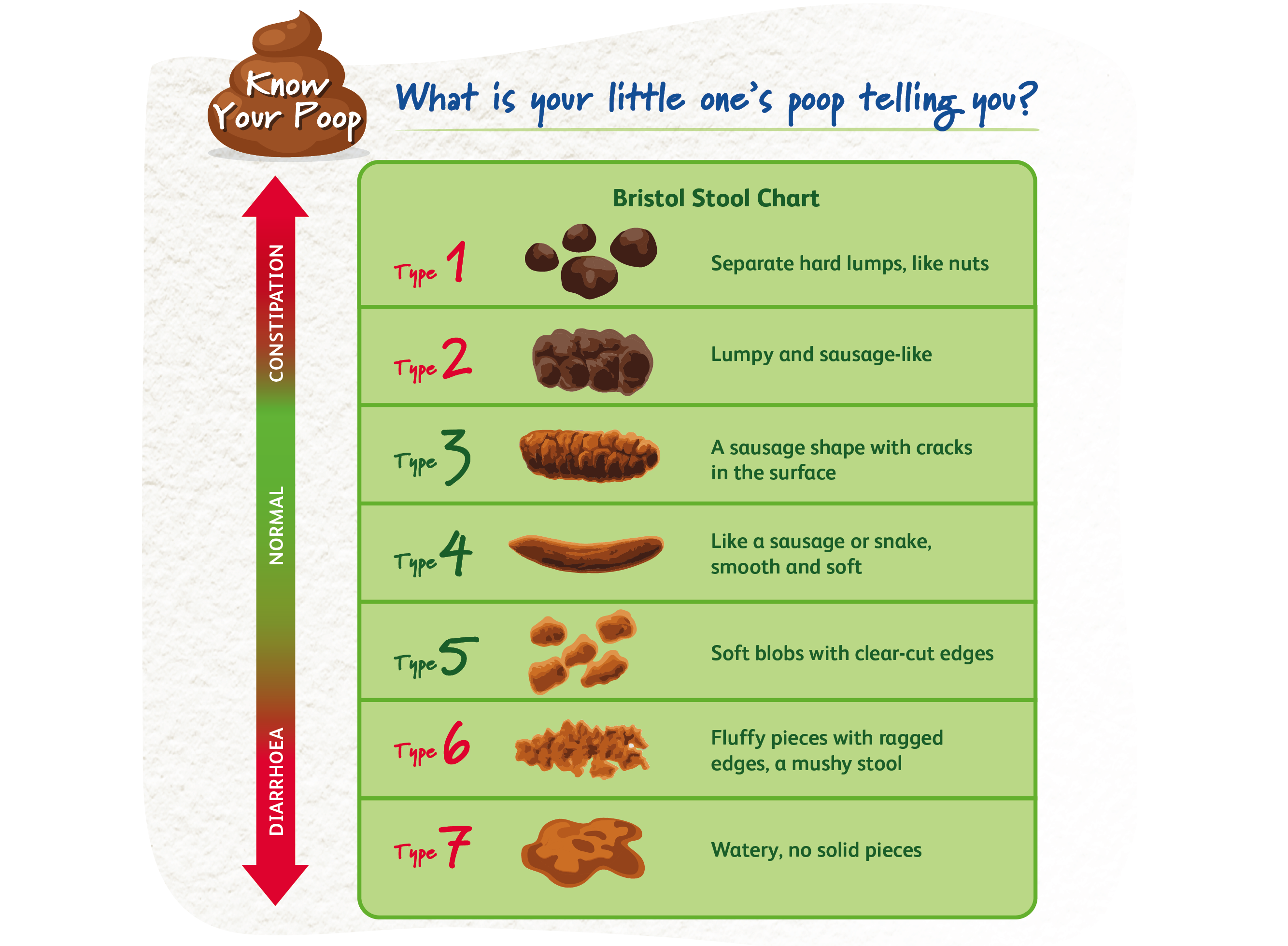
Safe, gentle and effective support for constipation relief.

Nutritional Breakdown
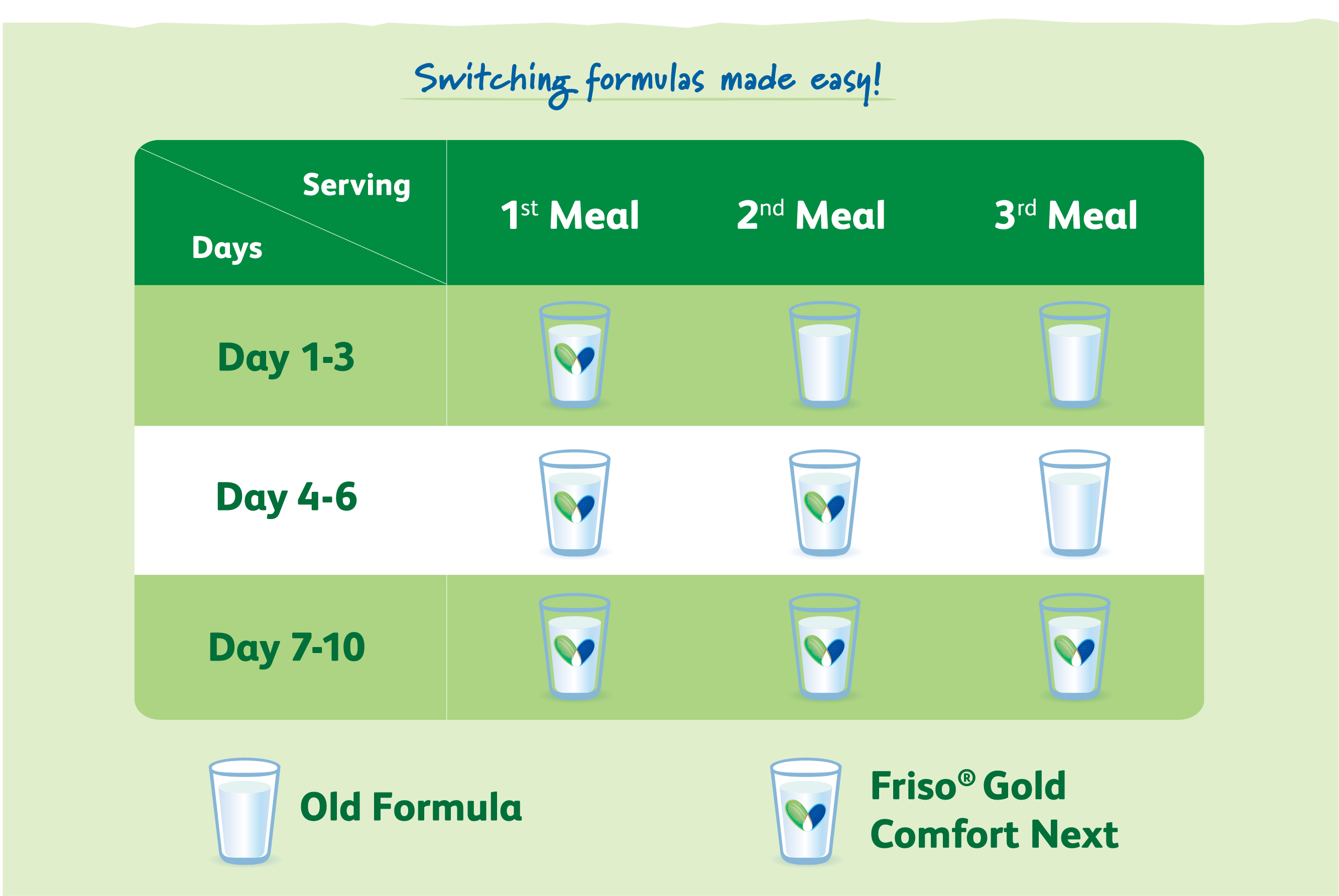
How to switch milk formulas:
When you've chosen a new milk formula to switch your child to, gradually transition their milk intake over the course of one to two weeks. The following table provides a quick guide on how to switch from your current formula to Friso® Gold Comfort Next:
As parents, trying to find the most suitable milk formula for your child's still-delicate little tummies can be a daunting task. You will need to compare the ingredients of each brand and formula type, then work to find the right flavour for their taste, while balancing the monetary cost.
This may take some time to learn and experiment, so be patient! It is also important to verify and check how each milk formula was sourced and produced for greater peace of mind when you are looking to provide your child with the most suitable and safe milk formula.
While we strive to make this guideline as reliable as possible, we recommend seeking advice from your preferred paediatrician if you have any questions or concerns to clarify.
The information provided is for general knowledge only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Please consult your healthcare professional before using this product.
*Natural milk source.
**Formula used for 8 weeks with decreasing pharmacological treatment during the first 4 weeks.
Sevilla DAC, et al. BMC Pediatr. 2022;22(1):672.
1. Manios Y, et al. BMC Nutr. 2020;6:46. | 2. Waller PA, et al. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;46(9):1057–1064. | 3. Georgieva M. World J Clin Pediatr. 2016;5(1):118-27. | 4. Vivatvakin B, et al. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2003;12(2):193-7. | 5. Moro G, et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002;34:291-5. | 6. Ben XM, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:6564–8. | 7. Uauy R, et al. Role of nucleotides in intestinal development and repair: Implications for infant nutrition. J Nutr. 1994;124(Suppl 8):1436S–1441S. | 8. Fazil SNS, et al. Malays J Pediatr Child Health. 2025;31(S1):15-20.
